Tasking: Fibonacci
A simple example of computing the Fibonacci sequence with a task dependency-based runtime system using HiCR. This example utilizes Pthreads to create processing units (workers) and Boost to create execution states (tasks). This test demonstrates the performance of a runtime system that executes a large number of lightweight tasks and showcases the capability to suspend tasks.
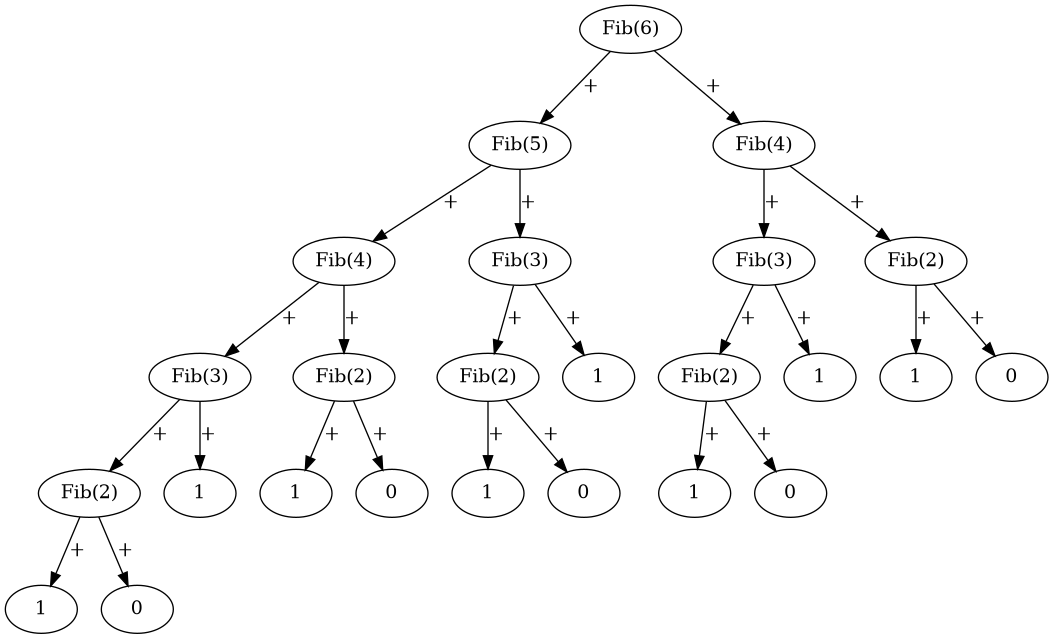
Each call to the Fibonacci(n) function generates two tasks to calculate Fibonacci(n-1) and Fibonacci(n-2). Fibonacci(n) will remain suspended until these tasks are completed. The recursion terminates when Fibonacci(1)=1 and/or Fibonacci(0)=0 is reached.
Below is a visual representation of Fibonacci(6)=8, which creates a total of 25 tasks.